IATA: Strong post-pandemic air cargo market expected
11 / 05 / 2021

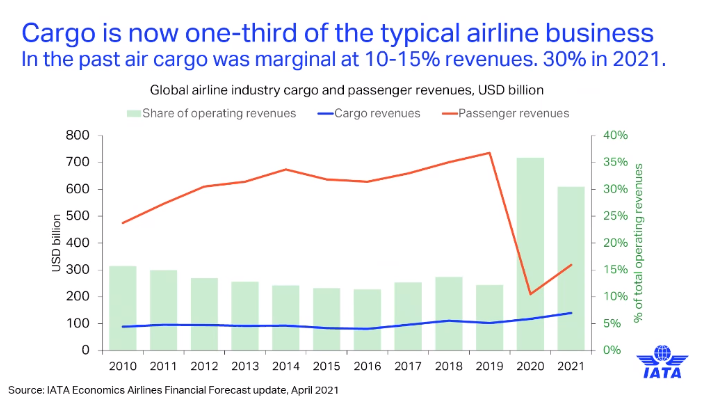
IATA is predicting a positive outlook for air cargo demand and believes it will continue to improve as the vaccine rollout progresses and bellyhold services pick up.
Kickstarting a press conference earlier today, Willie Walsh, director general of IATA, said airlines “deserve great credit” for pivoting their business focus away from passenger operations and towards airfreight in a short period of time.
Noting the use of preighters, Walsh said: “Airlines demonstrated great agility in responding to demand to ensure that there was sufficient supply to meet critical supply chain issues during the pandemic.”
He added that as passenger services pick up while the global vaccine rollout progresses, airlines will “shift from survival mode to rebuilding”.
“As that happens, we’ll continue to be very focused on the environmental issues that have not in any way bated since we’ve gone through this crisis,” he said.
“There is also an immediate focus on the development of sustainable aviation fuels.”
Data will also be essential in air cargo’s development.
Walsh said: “Better data enables us to improve our environmental performance. Better data enables us to assess the risk in a better way and that enables us to improve our safety performance.”
Market outlook
Brian Pearce, chief economist at IATA, said air cargo’s recovery from the pandemic is “good” and airfreight services remain in strong demand.
He said: “Shippers and companies need air cargo to rapidly transport components and final products to market as the global economy recovers. This has had a positive impact on the cargo tonne km (CTK) flow.”
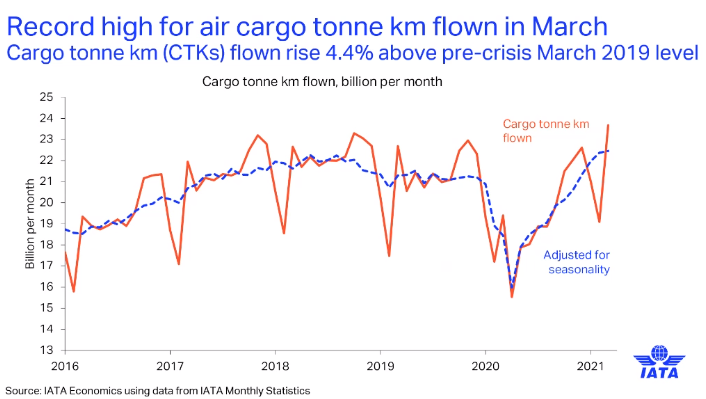
However, recovery is not equally strong on all trade lanes.
Pearce said fast improving trades include Middle East-Europe and Middle East-Asia.
Additionally, recovery in the North Pacific “reflects the fact that we’re seeing very strong Chinese and US economies, and that’s generating a lot of trade”.
By contrast, as a result of lockdowns, Europe has experienced a weakened economy, so its key trade lanes have not recovered as strongly.
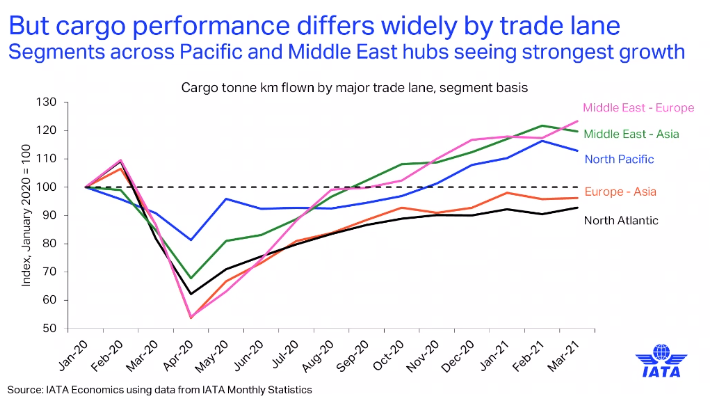
North America-based airlines have performed well in terms of volumes — they are around 20% up on pre-crisis (2019) levels.
Pearce noted that this contrasts with the slow recovery in Latin America and he attributed this to the “lack of support” given by governments, compared with the support received by North America-based airlines.
“We’re now seeing a number of Latin America-based carriers reorganising or under bankruptcy protection and as a result, they’re losing market share,” said Pearce.
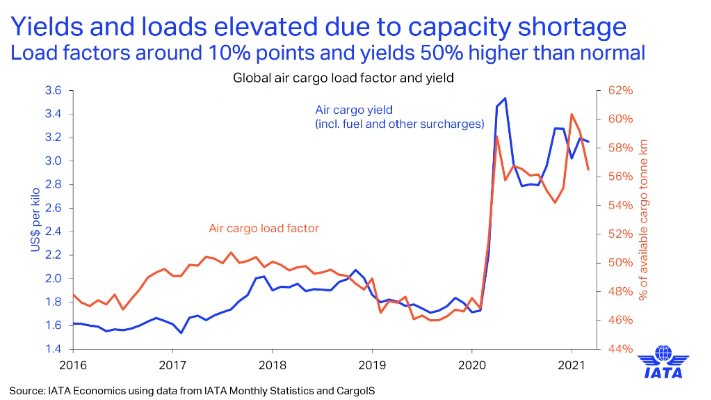
Pearce observed that over the last year load factors have been high — some 10 percentage points higher than they normally have been.
“There has been a severe capacity shortage in the industry because typically 50% or so of cargo would be carried in the holds of passenger aircraft,” said Pearce. “Travel restrictions have led to very high loads on aircraft that have been able to fly.”
This has resulted in higher yields, as Pearce noted: “That’s clearly benefited the revenues of the airlines operating in that business, as well as the ones that have pivoted to that business.”
However, Pearce thinks high load factors and high yields are probably going to be temporary.
“We [at IATA] think they’ll continue this year, but they reflect the unusual situation [of the pandemic],” he said. “As travel barriers come down, that situation will normalise.”
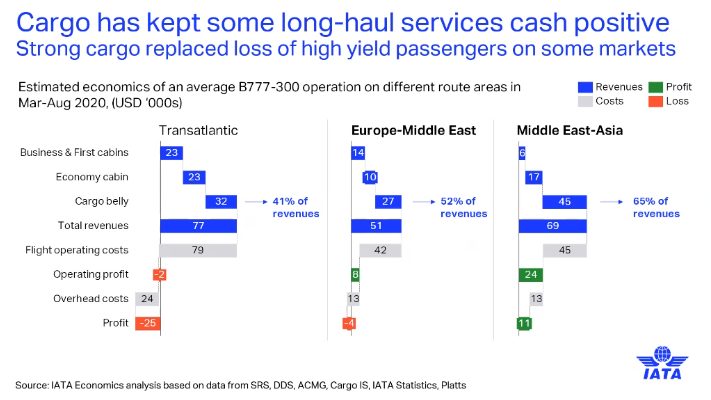
Pearce also said cargo sustained the connectivity of some long-haul passenger routes — even across the transatlantic market.
Looking forward, Pearce said: “We’re expecting air cargo to outperform other modes of transport. We saw similar trends following the global financial crisis.